Master of Divinity Programme
Master of Divinity: The M. Div. is a two/three year course programme, primarily designed to develop Christ-centered, Mission-Oriented leaders with academic excellence and ministerial skills to be able to articulate and actualize mission of God for bringing transformation in both churches and communities.
Curriculum: Curriculum of the two year Master of Divinity programme consists 12 core© subjects and 8 – 10 optional subjects. Curriculum of the Three year Master of Divinity programme consists 18 core© subjects and 12 – 14 optional subjects. The subjects along with its descriptions are placed below.
Master of Divinity Course List
| First Year, Semester 1 | Credit Hour |
|---|---|
| 1. Introduction to the Old Testament© | 3 |
| 2. Introduction to Missions & Evangelism | 3 |
| 3. Introduction to Missions & Evangelism | 3 |
| 4. Research Methodology | 3 |
| 5. Spiritual Formation | 3 |
| 6. English | 3 |
| First Year, Semester 2 | Credit Hour |
|---|---|
| 7. Introduction to the New Testament© | 3 |
| 8. History of Christianity© | 3 |
| 9. History of Israel | 3 |
| 10. Christian Education | 3 |
| 11. Biblical Interpretation | 3 |
| Second Year, Semester 1 | Credit Hour |
|---|---|
| 12. Preliminary Hebrew© | 3 |
| 13. History of Christianity in Asia with special Emphasis on India© | 3 |
| 14. Introduction to Communication: Theory and Practice© | 3 |
| 15. Modern Religious and Secular Movements© | 3 |
| 16. Person and Work of Christ© | 3 |
| 17. Cultural Anthropology | 3 |
| Second Year, Semester 2 | Credit Hour |
|---|---|
| 18. Preliminary Greek© | 3 |
| 19. Advanced Homiletics© | 3 |
| 20. Advanced Study of Pentateuch | 3 |
| 21. Survey of Major Religions© | 3 |
| 22. Women in the Church and Society | 3 |
| 23. History of Christian Missions | 3 |
| Third Year, Semester 1 | Credit Hour |
|---|---|
| 24. Biblical Theology© | 3 |
| 25. Pastoral Theology© | 3 |
| 26. Christian Ethics© | 3 |
| 27. Advanced Study of Gospels | 3 |
| 28. Christian Apologetics | 3 |
| 29. Biblical Theology of Mission | 3 |
| Third Year, Semester 2 | Credit Hour |
|---|---|
| 30. Theology in the Asian context with special emphasis on India© | 3 |
| 31. Church Administration & Leadership© | 3 |
| 32. Principles of Church Planting and Church Growth | 3 |
| 33. Community Development and Social Change | 3 |
| 34. Leadership Development | 3 |
| 35. Comprehensive Examination | 3 |
Course Description
Biblical Studies
1. Introduction to the Old Testament: An overview of the Old Testament that sets its books in the context in which they were produced.
2. Introduction to the New Testament: An overview of the New Testament that sets its books in the context in which they were produced.
3. Preliminary Greek: An introduction to Biblical Greek, intended to provide students with the necessary knowledge of the language that will enable them to be able to use basic tools like lexicons.
4. Preliminary Hebrew: An introduction to Biblical Hebrew, intended to provide students with the necessary knowledge of the language that will enable them to be able to use basic tools like lexicons.
5. Biblical Interpretation: An introduction to the task of interpreting the Bible in its context and in a way that is relevant to the contemporary context.
6. Biblical Theology: A study of the theological themes of the Bible that is based on the unity of the two testaments.
7. Advanced Study of Pentateuch: A study of Genesis through Deuteronomy focusing first on surveys of books as a whole, then interpretation of parts of books in the context of books as wholes, and finally on the synthesis of books. Exegetical study presumes the student’s reasonable prior grasp of the Hebrew language.
8. History of Israel: A study of the origin, development and major events of the nation Israel until the birth of Jesus Christ. Emphasizes God’s redemptive work through the nation of Israel.
9. Advanced Study of Gospels: A Study of the four Gospels with a view to understand the life and teachings of Jesus Christ. Exegetical study presumes the student’s reasonable prior grasp of the Greek language.
Theology and Ethics
10. Introduction to Systematic Theology: An overview of the major doctrines of the historic Biblical faith.
11. Person and Work of Christ: An introduction to the doctrines of the person and work of Christ that includes a historical survey of Christological debate in the Church.
12. Christian Ethics: An introduction to the basic principles of Biblical ethics and how they apply in modern contexts.
13. Theology in the Asian Context with Special Emphasis on India: An introduction to contextual theologies in Asia, with special emphasis on India.
History of Christianity
14. History of Christianity: A survey of the history of Christianity and doctrinal development of the church from the apostolic age to the present day. The course looks carefully at church – state relationships, the internal organization of the Church, the Roman Primacy, people domination and doctrinal controversies within the early and medieval periods.
15. History of Christianity in Asia with Special Emphasis on India: A survey of the spread of the Christian faith across the continent of Asia, and its impact on its peoples, their customs and cultures
Religion and Society
16. Survey of World Religions: An introductory study of the major religions of the world, with an emphasis on those that are predominant in the sub-continent.
17. Modern Religious and Secular Movements: A survey of modern religious and secular movements in India, and contemporary trends.
18. Community Development and Social Change: This course provides a sociological analysis of community and explores community development models and the history of community development practices. Students would develop skills to work in community-based organizations and institutions. This course includes a required service learning component with a locally-based community organization
Missions and Evangelism
19. Introduction to Missions and Evangelism: An introductory study of the biblical and theological basis for the mission of the Church.
20. Introduction to Communication – Theory and Practice: An introduction to the basic principles of communication, especially in relation to the task of bearing witness to the good news of Christ.
21. History of Christian Missions: Surveys a history of the missionary work of the church from the beginning until the present day. Emphasis is given to trends, issues, strategies and methods of the movement. The course gives the students a broad outlook and sympathetic understanding of the church’s worldwide task.
22. Cultural Anthropology: An analysis of culture, personality, socialization, status, roles and the social institutions of family, education, religion, government and economy – particularly as applied to cross-cultural missions.
23. Principles of Church Planting and Church Growth: Studies the biblical mandate for life and ministry in the church. The course looks at the procedures for planning new churches and growing existing churches. Specific topics include church structure, forms of worship, self-support, lay participation, leadership development, and church-mission and denomination relationships.
24. Biblical Theology of Mission: A study of principal texts in the Old and New Testaments dealing with mission, evangelism, discipling, and renewal, with attention to relevant scholarly debate regarding their significance. Major biblical-theological themes of missiological importance are dealt with using scholarly approaches for their meaning and significance in the understanding and practice of Christian mission.
Christian Ministry
25. Spiritual Formation: A survey of essential elements to nurture spiritual disciplines for the church minister, including an introduction to necessary tools and practices of spiritual formation and Christian holiness.
26. Christian Education: A critical discussion of a biblical perspective of education and the church’s biblical ministry of reaching and teaching all ages. Current methods and approaches are critically discussed and practical aspects including curriculum, material, organization and administration are presented.
27. Advanced Homiletics: Familiarizes the student with basics of sermon preparation and delivery. Opportunity is given to students to practise sermonizing including planning, pulpit etiquette, and mannerism. Special attention is given on the preparation and delivery of expository preaching.
28. Pastoral Theology: This is a study of the call, qualifications, and necessary character of the minister. Special attention is given to the pastor as a person of discipline, development, and dedication. The study focuses on the theory and practice on the pastoral ministries on ordinances, funerals, weddings, child dedication, church dedication, house dedication, house visitation, counselling, and making disciples.
29. Church Administration and Leadership: This course emphasizes the role of administration as a necessary function in pastoral ministry. Subjects addressed include: modern management principles to church leadership, investigates strategic thinking/planning, crisis management, office and time management; personnel resources, proper financial procedures, membership register maintenance, church discipline, and the other social and spiritual aspect of church.
General Studies
30. Research Methods: Prepares the student for writing the long essay by studying the various methods of appropriate research and showing how research findings should be announced in writing. Considerable attention is given to library research
31. Leadership Development: An interdisciplinary course designed to introduce the student to the tasks, strategies, skills and biblical principles of effective leadership. Course activities will move the student from theory to the practical processes of leadership.
32. Women in Church and Society: Studies the biblical, historical and contemporary involvement of women in the Christian Ministry. It examines the biblical, theological, and socio cultural issues related to female roles in ministry, missions and in the local church.
33. Christian Apologetics: This course is designed to generate confidence concerning the Christian faith through a rational defence and response to the anti-Christian objections. Attention is given to a variety of Christian evidences that support the claims of Christianity.
34. English: Review of English grammar and literature, vocabulary building, and the enhancement of writing skills. (May be skipped if the student can demonstrate sufficient competency at the time of entrance test).
35. Comprehensive Examination: Comprehensive examination will be conducted to the M. Div. final year class just before their graduation. The questions will be set from the six departments: Biblical Studies, Mission, Christian Ministry, Christian Theology, Religions, and Christian History. A student must pass the comprehensive examination to be graduated.
Grading System
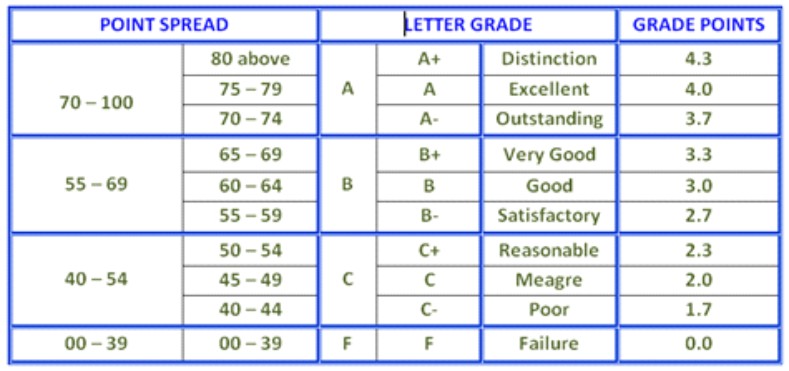
Promotion
A student must obtain a minimum 40% or above in each subject to be promoted. Students failing in more than 3 subjects in a semester will not be promoted. However, students failing in one to three subjects in a semester will be promoted with provision made for a re-take examination.
Graduation Requirements
- Master of Divinity two year students should complete minimum 20 subjects (60 credit units).
- Master of Divinity three year students should complete 30 subjects (90 credit units).
- Successful completion of ministry Internship with minimum of a GPA of B.
- Satisfactory development of character and spiritual life.
- Clarification of all college fees.
